Skip Zone
ADDPMP754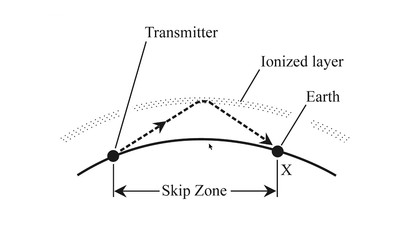
The skip zone is a natural phenomenon that cannot be influenced by technical means. It is an annular region between the farthest points at which the ground wave can be received and the nearest point at which the refracted sky waves can be received. Within this region, no signal can be received because, due to the conditions of the local ionosphere, the relevant sky waves are not reflected but penetrate the ionosphere. Transmitting at night is most effective for long-distance communication but the skip zone becomes significantly larger.
A method of decreasing the skip zone is by decreasing the frequency of the radio waves, as decreasing the frequency is akin to increasing the ionospheric width. A point is eventually reached when decreasing the frequency results in a zero-distance skip zone. In other words, a frequency exists for which vertically incident radio waves will always be refracted back to the Earth. This frequency is equivalent to the ionospheric plasma frequency.