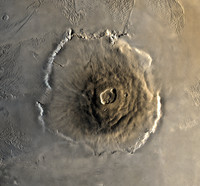
Bell-mouth spillway
ADDPMP644
Uncontrolled open channel spillways, used to control and convey impounded water from a dam or levee, in order to prevent dam failure. Bell-mouth spillways are designed like an inverted bell, where water can enter around the entire perimeter. They are also called morning glory (after the flower) or glory hole spillways.
In some cases, bell-mouth spillways are gate-controlled. This is the case of the bell-mouth spillway of Hungry Horse Dam in Montana, U.S., the highest structure in the world, which is controlled by a 64-by-12-foot (19.5 by 3.7 m) ring gate.
Other well-known bell-mouth spillways include the one in Covão dos Conchos reservoir lake, Portugal, which is constructed to look like a natural formation or the one in Geehi Dam, Australia, for being the largest bell-mouth spillway in the world, with a 105-ft (32-m) diameter at the lake’s surface.