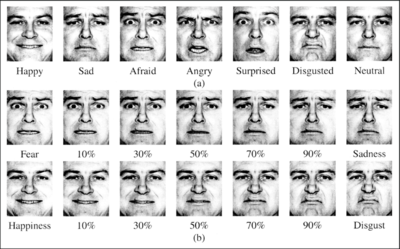
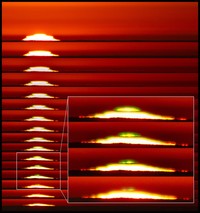
Ekman 60 Faces Task
ADDPMP712In The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals published in 1872, English naturalist Charles Darwin theorised that emotions were evolved traits universal to the human species. However, the prevalent belief during the 1950s, particularly among anthropologists, was that facial expressions and their meanings were determined through behavioural learning processes.
In the 1970s, American psychologist Paul Ekman found, through a series of studies, a high agreement across members of diverse western and eastern literate cultures on selecting emotional labels that fit facial expressions. According to him, universal emotions included wrath, grossness, fear, joy, loneliness and shock. Findings on contempt were less clear, though there is at least some preliminary evidence that this emotion and its expression are universally recognised.
Ekman’s famous test of emotion recognition, the Pictures of Facial Affect (POFA) stimulus set, was published in 1976. Consisting of 110 black and white images of Caucasian actors portraying the six universal emotions plus neutral expressions, the POFA has been used to study emotion recognition rates in normal and psychiatric populations around the world. Ekman himself used these stimuli in his original cross-cultural research.
Working with American psychologist Wallace V Friesen, Ekman demonstrated that the findings extended to preliterate Fore tribesmen in Papua New Guinea whose members could not have learned the meaning of expressions from exposure to media depictions of emotion. Ekman and Friesen then demonstrated that certain emotions were exhibited with very specific display rules and culture-specific prescriptions about who can show which emotions to whom and when. These display rules could explain how cultural differences may conceal the universal effect of expression.
In the 1990s, Ekman proposed an expanded list of basic emotions including a range of positive and negative emotions that are not all encoded in facial muscles. The newly included emotions were: amusement, contempt, contentment, embarrassment, excitement, guilt, pride in achievement, relief, satisfaction, sensory pleasure and shame.