Olympus Mons
ADDPMP441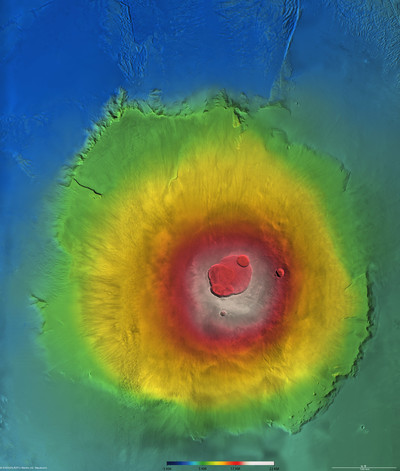
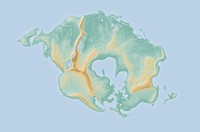
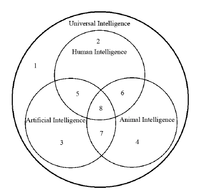
Olympus Mons is a very large shield volcano on the planet Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21 km as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a half times Mount Everest’s height above sea level. It is one of the largest volcanoes, the tallest planetary mountain, and the second tallest mountain currently discovered in the Solar System.
The volcano is located in Mars’ western hemisphere, with the center at 18°39′N 226°12′E, just off the northwestern edge of the Tharsis bulge. The western portion of the volcano lies in the Amazonis quadrangle (MC-8) and the central and eastern portions in the adjoining Tharsis quadrangle (MC-9).
Two impact craters on Olympus Mons have been assigned provisional names by the International Astronomical Union. They are the 15.6 km (9.7 mi)-diameter Karzok crater (18°25′N 228°05′E) and the 10.4 km (6.5 mi)-diameter Pangboche crater (17°10′N 226°25′E). The craters are notable for being two of several suspected source areas for shergottites, the most abundant class of Martian meteorites.